
The Omega Workshop was a curious idea set up in 1913 by Roger Fry. It was really following Fry’s rise as a rebel in the art world. Though hard to think of as controversial now, in 1910 he held the first British exhibition of the Post-Impressionists to some upraw.

It featured Gauguin, Van Gogh and Matisse. He then followed this with another exhibition in 1912 of Cézanne, Matisse and Picasso. These exhibitions are noted with contemporary accounts of Slade art teacher, Henry Tonks, forbidding his students from going to it as it might corrupt their mind; and it did just that, for many of them like Mark Gertler and Dora Carrington it changed their styles of painting and bought them into the Bloomsbury groups orbit.
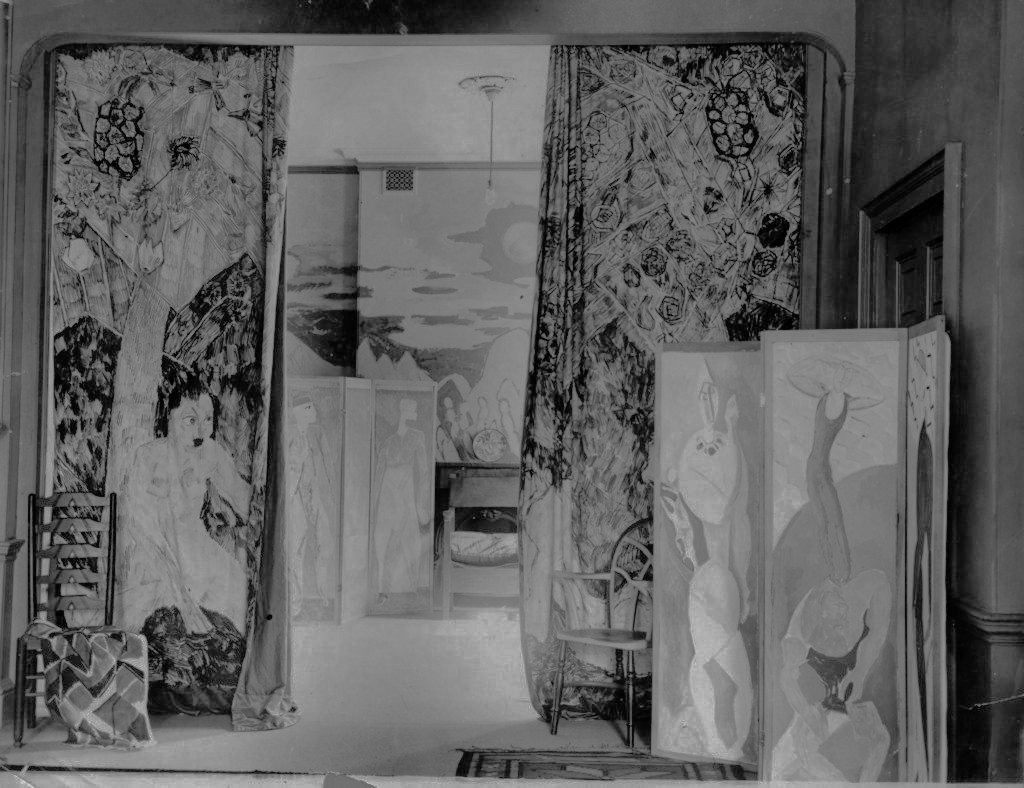

The Omega Workshop Studios
The Omega Workshop was an attempt to celebrate handmade items, without being too rooted in the Arts and Crafts tradition. Though the link is undeniable, the decorations of the items was not precise and Omega was more like the British version of the Mingei movement that happened later in Japan. On visiting the Omega studios in 1913 Yone Noguchi noted that Roger Fry was “attempting to create an applied art just as (William) Morris did” and that the studio was using Cubist motifs and designs, of abstract shapes in the fabrics and wood marquetry.

Room at 4 Berkeley Street, Painted by Omega Workshops.
What Roger Fry brought to the workshop was an inquisitive nature on designs from Africa as well as encouraging the artists to look at the works of other modern painters like Kandinsky. The main success of all these abstractions is that the studios were an area were the artists could play with ideas, as well as an exhibition space for their outcomes. They would give themselves a basic education on the method of the craft, say rug weaving, and then look at the limitations of the process and work designs around this.
Though the projects originally included Wyndham Lewis, he went off to explore the other outcome of European cubism – futurism. The main contenders were Roger Fry, Vanessa Bell, Duncan Grant, Simon Albert Bussy, Roald Kristian, Edward Wolfe, Edward McKnight Kauffer, Frederick Etchells, Winifred Gill, Henri Doucet, Nina Hamnett.

The rug (below), and used in this postcard (above) was made for Lady Hamilton, by Royal Wilton Carpets, for Omega Workshops by Vanessa Bell.

Vanessa Bell – Rug for Lady Hamilton, 1914
As the studios printed and made their own publicity material, they also started to print books. One if their earliest was by Arthur Clutton-Brock’s Simpson’s Choice, 1915. It had printed boards with a geometric design and woodcuts by Roald Kristian. Clutton-Brock worked as a reviewer and critic for The Times and was a personal friend of Roger Fry, it was this type of journalist the workshops needed on their side.
Soon after Leonard and Virginia Woolf were looking into hand-printing and bought a box of type blocks, a printing machine, and where printing their own books (though later they did employ a typesetter). They featured the prints of artists at the Omega Studios, though they were printed on the table at Hogarth House, the close connections ties them to the Omega Workshops.
In March 1917, the Woolfs walked along Farringdon Street, London, and purchased a printing machine, materials and an instruction booklet from Excelsior Printing Supply Company. The purchase was impulsive, but they had been discussing the idea of setting up a printing press since autumn 1916. Although the Woolfs were enthusiastic and absorbed by the work, their first publication shows some signs of amateurism such as irregular spacing and blotted ink. As Hermione Lee highlights, however, the Woolfs quickly developed into professional printers.
It took two and a half months to print 150 copies of Two Stories, which was released for sale in July 1917. Because the printing process was all-consuming, Virginia did not compose ‘The Mark on the Wall’ until the printing of Leonard’s story was complete. The 32 pages were sewn together and bound with paper covers by hand. Being bound on an ad-hoc basis, different covers exist: the British Library’s copy is bound in a blue weave-textured material.
Below is one of the Woolf’s early books, from Two Stories, The Mark on the Wall, by Virginia Woolf, with woodcuts by Dora Carrington.

The Mark on the Wall, by Virginia Woolf, 1917
The pottery that Omega originally decorated was bought in, but soon he asked a pot asked someone to make pots for them. “He contacted George Schenck , a potter at Mitcham , Surrey , and tried to get him to throw the simple shapes he wanted . The potter was unable to alter his long – practised throwing and Roger realized he would have to learn to do it himself “. Then on Schenck gave Fry pottery lessons were he experimented with designs and glazes, rather than using household paint applied onto vases. Later in 1915 when Fry designed a table service production was moved to Carter & Co, Poole, (later to become Carter Stabler and Adams, and Poole Pottery). At this time Carter & Co were making designs for garden pots for Liberties and were a high class artisanal pottery. Many of the works potted had a chinese influence.

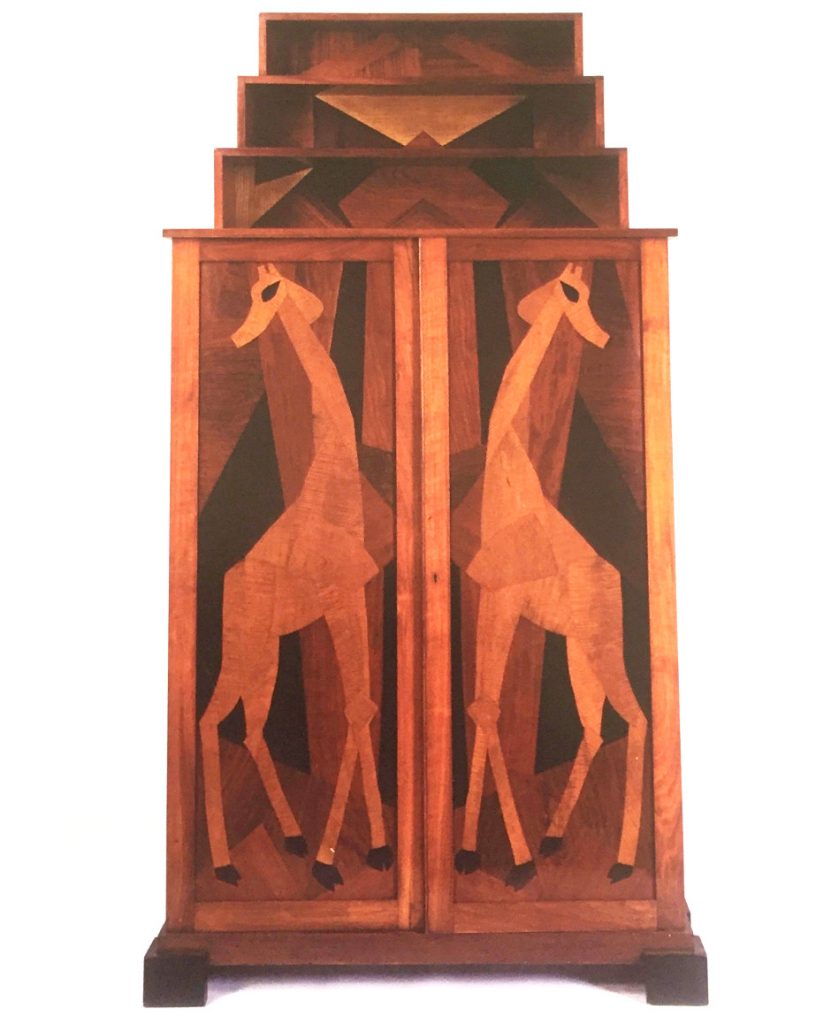
When it comes to the furniture, many companies were employed to make pieces, for different uses, the marquetry cabinet here John Joseph Kallenborn.

Dryad made the cane seating and the chairs that were later painted by the workshop members.
I attach a write up by Roger Fry here, not to offend, as it is contemporary language about historical artifacts, but rather to show how many inspirations Fry was feeding off and his aims.
If you look at a pot or a woven cloth made by a negro savage of the Congo with the crude instruments at his disposal, you may begin by despising it for its want of finish. If you put them beside a piece of modern Sevres china or a velvet brocade from a Lyons factory, you will perhaps begin by congratulating yourself upon the wonders of modern industrial civilization, and think with pity of the poor savage. But if you will allow the poor savage’s handiwork a longer contemplation you will find something in it of greater value and significance than in the Sevres china or Lyons velvet. It will become apparent that the negro enjoyed making his pot or cloth, that he pondered delightedly over the possibilities of his craft and that his enjoyment finds expression in many ways; and as these become increasingly apparent to you, you share his joy in creation, and in that forget the roughness of the result. On the other hand the modern factory products were made almost entirely for gain, no other joy than that of money making entered into their creation. You may admire the skill which has been revealed in this, but it can communicate no disinterested delight. The artist is the man who creates not only for need but for joy, and in the long run mankind will not be content without sharing that joy through the possession of real works of art, however humble or unpretentious they may be.
The Omega Workshops, Limited is a group of artists who are working with the object of allowing free play to the delight in creation in the making of objects for common life. They refuse to spoil the expressive quality of their work by sand-papering it down to a shop finish, in the belief that the public has at last seen through the humbug of the machine-made imitation of works of art. They endeavour to satisfy practical necessities in a workmanlike manner, but not to flatter by the pretentious elegance of the machine-made article. They try to keep the spontaneous freshness of primitive or peasant work while satisfying the needs and expressing the feelings of the modern cultivated man.
ROGER FRY, Director, Omega Workshops, Ltd.
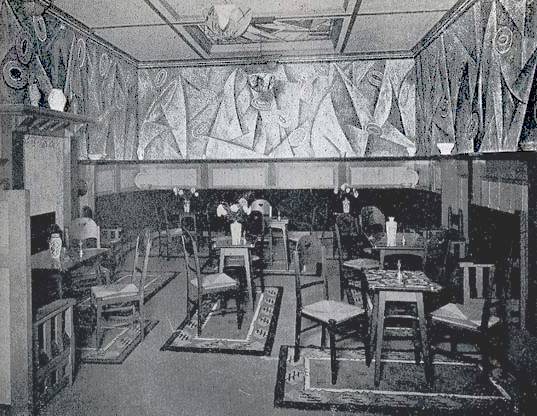

Room decorated by Omega Workshops for the Cadena Cafe, 59 Westbourne Grove, London. The rugs, attributed by Roger Fry but likely designed by Frederick Etchells with chairs made for Roger Fry by Dryad.
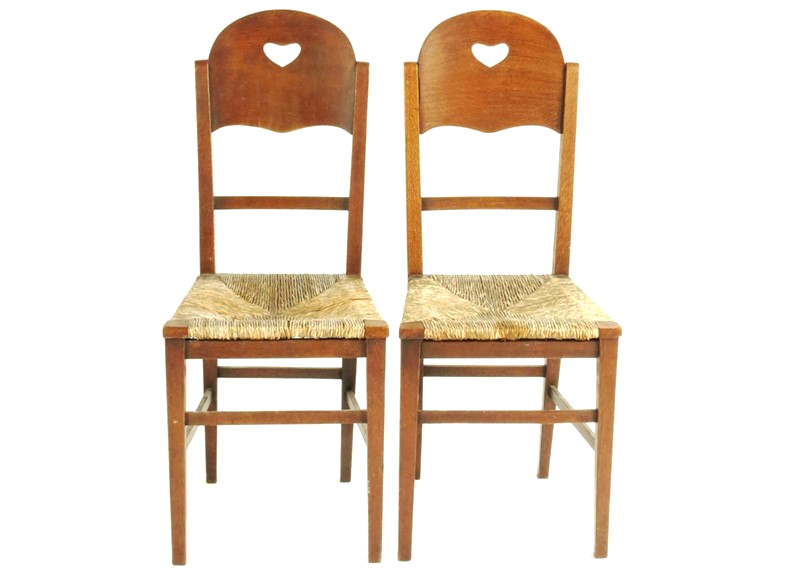
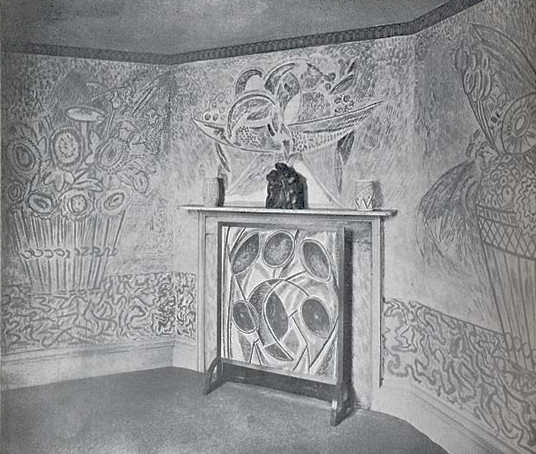


Henry Harris’s house in Bedford Square by Omega Workshops.
Maybe part of the biggest failures of the group was the building they set themselves up in. George Bernard Shaw’s concern voiced to Fry in May 1914 was that “you need a shop window, Morris found that out. It is all very well to live in a quiet London Square and look like an Orthopaedic Institute, but the price you pay is that your business remains a secret of a clique.“




